What Are Foot Cramps a Sign of? Causes & Relief
Every person has probably experienced cramps at least once in their life—involuntary wave-like contractions of muscles that can be accompanied by numbness or severe pain. Cramps begin suddenly and also stop spontaneously. Attacks can be isolated or repeated periodically.
If you suffer from frequent foot cramps and want to prevent them, we've included everything you need to know below.
What Are Foot Cramps?
They are involuntary, painful, short-lasting muscle contractions that occur suddenly and unexpectedly. Their origin may involve metabolic or neurological disorders, overexertion, overloads, etc. They appear after intense and exhausting exercises but can even appear at rest. They differ from muscle fasciculations since they are minor muscle contractions in the area of a muscle group supplied by a single motor nerve fiber, and they can go unnoticed.
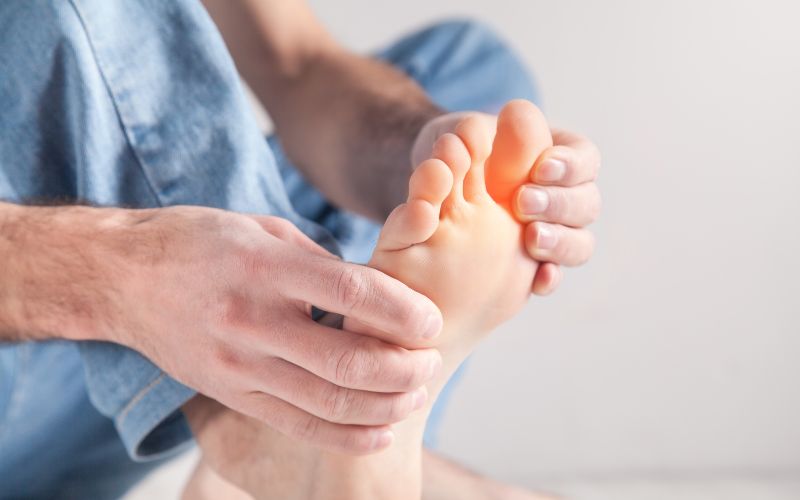
Symptoms of Foot Cramping
Cramps can strike anywhere in your foot- from the arch, toes, or right down to your heel, and each has a slightly different kind of ache. Foot cramps typically last several seconds to minutes, with gradual subsidence, though soreness lingers. Here's what you may find yourself experiencing during an episode:
Sharp pain: It can feel like a stabbing pain because the onset of cramps is sudden.
Stiffness and tightness: Muscles in the foot may feel rigid and unyielding.
Hard to the touch: The affected area becomes noticeably firm.
Arch involvement: Cramps often target the arch, making it an area of particular concern.
Can Certain Diseases Cause Foot Cramps?
The absence of some vital vitamins and minerals, including vitamin D and magnesium, is among the essential factors contributing to muscle function issues that trigger night cramps. Several background conditions precipitate foot cramps, and knowing these will help address and prevent those annoying episodes.
Diabetic Neuropathy
One of the common ones is diabetic neuropathy, a common complication of diabetes that causes nerve damage in all parts of the body. Nerve damage from very high glucose levels in the blood could lead to shocking foot cramps.
Peripheral Arterial
Another medical condition that causes foot cramps is peripheral arterial disease. In this condition, the arteries supplying blood to the limbs shrink or are blocked, thus reducing blood flow. When one does not have proper circulation, they are likely to experience foot and hand cramps, especially when moving.
Mineral Deficiencies
Medical causes of cramps in the feet and other muscles include deficiencies in some minerals and electrolytes, such as potassium, calcium, and magnesium. These cramps usually manifest themselves as being linked with many other serious medical conditions, such as kidney failure and hormonal disorders.
Venous problems
Venous problems like varicose veins can also be linked to foot cramps. Blood pooling in the veins due to poor circulation can trigger pain and cramps. Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease is an autosomal dominant genetic disorder of the peripheral nerve that leads to muscle weakness, cramps, and pain in the leg and feet.
Why Do My Feet Get Cramps At Night?
Nighttime foot cramps, or nocturnal cramps, are a painful and frustrating experience many people suffer from.
Dehydration: This is usually caused by dehydration, in which bodily fluids result in an imbalance of electrolytes, mainly potassium, calcium, and magnesium.
Lack of stretching and exercise: Another factor contributing to night cramps is a lack of stretching or exercise. If muscles are not adequately stretched, especially after a day of intense activity, they can become tight and more prone to cramps. Also, staying in one position for a long time, such as sitting or standing for hours, can cause muscle fatigue, increasing the chance of night cramps.
Sleeping position: It can also trigger cramping. Sleeping with your feet improperly may provoke contraction within the calf and foot muscles and eventually cause pain. Poor blood circulation can also lead to cramping because your legs are crossed or you have unfavorable bed sheets.
Age: Another reason is old age; older people are more prone to joint problems and night cramps than young people. Older adults start losing their elasticity with time and have relatively poor nerve functions, hence the vulnerability to such attacks.
Medical condition: Other conditions can also predispose one to night cramps. Examples are diabetes, peripheral artery disease, and multiple sclerosis. This is through the problems they cause with circulation and nerve damage.
Who Suffers From Cramps More?
People who take diuretics (which can cause a loss of minerals) and those with a family history of cramps are also more likely to suffer from them.
Cal-Mag Liquid with Fulvic by Vital Earth Minerals is one of the best supplements to avoid cramps.
What To Do To Avoid Night Cramps?
Good prevention of night cramps calls for several measures that keep your muscles calm and well-hydrated.
- First, this would include staying hydrated all day long. Drinking plenty of water is supposed to balance the electrolytes in one's body, including nutrients for muscle health and cramp relief, such as potassium, calciumand magnesium, which enable the muscles to function properly.
- Stretching before bed is another good way to go. Stretch the muscles within your legs and feet lightly, reducing tension developed throughout the day and minimizing the likelihood of spastic contractions at night, andhelping to fall asleep peacefully.
- Concentrate stretches upon the calf and foot muscles, holding each for at least 30 seconds.
When To See A Doctor
If you are experiencing frequent, severe, or chronic foot cramps, you may want to see a doctor. These symptoms may interfere with your activities or your sleep, but they may also indicate an underlying condition that should be looked into by a healthcare provider.
Here are some examples when you need to see a doctor:
Heavy and persistent cramps
Conclusion
If you're experiencing foot cramps, it's important to identify the root cause. They might signal dehydration, mineral imbalances, or overexertion. Consider whether your shoes fit well or if poor circulation could be a factor. Don't ignore persistent cramps; they might indicate nerve damage. Stay hydrated, maintain a balanced diet, and guarantee proper foot support. If cramps persist despite these efforts, it's time to consult a doctor to rule out more serious health concerns.
Frequently Asked Questions
Why Am I Getting So Many Cramps in My Feet?
Most of the causes are due to dehydration, poor shoe choices, muscle fatigue, or improper stretching techniques. Other causes include nerve compression, diet impacts, improper exercise routines, lack of foot support through shoes, or high levels of stress.
How can I relieve foot cramps at home?
To relieve foot cramps, try stretching the affected muscles, massaging the area, and applying heat or cold. Staying hydrated and ensuring a proper intake of nutrients, such as potassium, can help prevent cramps. In some cases, medications or therapies recommended by doctors may be needed for more severe cramps.
Can foot cramps be a sign of an underlying health issue?
Yes, foot cramps can be a symptom of a more serious health issue, such as hypokalemia, high blood pressure, or muscle problems in the legs. If cramps occur frequently or are accompanied by other symptoms, such as foot pain, it’s advisable to seek medical advice or visit a healthcare provider for further diagnosis.
Are foot cramps related to anxiety or stress?
Yes, anxiety and stress can sometimes trigger muscle spasms, including foot cramps. If anxiety is the cause, relaxation techniques, proper care, and advice from your doctor may help reduce occurrences.
How does pregnancy affect foot cramps?
Pregnancy can lead to muscle cramps due to increased pressure on the legs and changes in nutrient levels, especially in the later stages.

