Calcium's Impact on Digestive Function
1st Jul 2025
When most people hear “calcium,” they think of bones and teeth. However, this essential mineral does much more than build strong bones—it also supports many vital functions, especially digestion.
Calcium plays a crucial role in facilitating the passage of food through the gut and aiding the body in absorbing essential nutrients. In this guide, we’ll take a closer look at how calcium supports digestion and why getting enough of it every day matters for your health.
Support your body's natural balance with Vital Earth Mineral Blend.
The Role of Calcium in the Human Body
Calcium is an essential mineral for digestion and gut health; it's more than an element that builds bone strength - it's a major component of many important body processes. From enabling muscles to contract to assisting with nerve impulses and hormone regulation, calcium keeps your body functioning on a cellular level.
Although it is most commonly associated with bone and health, its impact extends to digestion, cardiovascular function, and even cellular communication. Learning about calcium's broader role can help you understand why it's essential to consume enough of it every day.
Basic Functions of Calcium
Calcium is the most abundant mineral in the human body, with nearly 99% of it stored in bones and teeth. However, the remaining 1% is crucial for functions such as muscle movement, nerve transmission, hormone release, and blood clotting. Your body needs a consistent calcium supply from food, liquid calcium or tablet calcium supplements to maintain these roles.
Importance Beyond Bone Health
Without a doubt, calcium plays a crucial role in maintaining bone health, and bone weakness is often linked to a calcium deficiency. However, calcium also supports critical systems such as the heart and gastrointestinal (GI) tract. Without enough calcium, many of your body's cellular functions, including digestion, could be thrown off balance.
10 Key Impacts of Calcium on the Digestive System
Calcium helps your digestive system function properly. It supports muscle movement in your stomach and intestines, helps your body make stomach acid, and activates enzymes to break down food. Without sufficient calcium, digestion can slow down, leading to problems such as bloating or constipation.
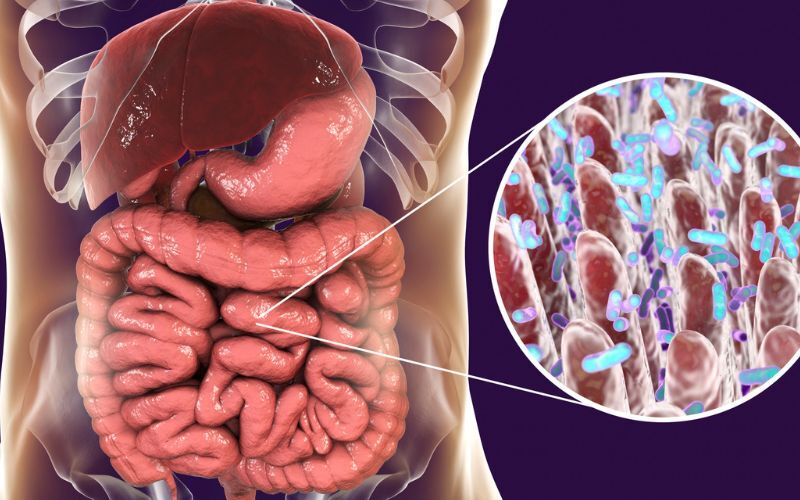
1. Supports Muscle Contractions in the Digestive Tract
Calcium helps to regulate the muscles that propel food through your digestive tract. This wave-like action, called peristalsis, relies on calcium for adequate strength and timing. When there's not enough calcium, these contractions can weaken or become irregular, leading to constipation or slower digestion.
2. Helps in Stomach Acid Regulation
It also helps your stomach produce the right amount of acid for breaking down food. By maintaining healthy levels of stomach acid, calcium facilitates smooth digestion and protects the stomach lining. Too little acid can cause bloating and reduce nutrient absorption, while too much can lead to discomfort.
3. Activates Digestive Enzymes
Certain enzymes in the digestive system need calcium to become active. These enzymes help break food into smaller parts so the body can absorb nutrients. If calcium is low, enzyme activity may slow down, making digestion less effective.
4. Aids in Nutrient Absorption
Calcium doesn't just help digest food—it also helps your intestines absorb other nutrients. It enhances the absorption of vitamins, such as B12, and minerals, like magnesium. If your calcium levels are too low, your body might not absorb enough nutrients, even from a healthy diet.
5. Maintains Gut Wall Strength
The cells that form the gut lining rely on calcium to stay strong and healthy. A strong gut wall protects your body from toxins and supports better nutrient absorption. A weak gut lining can lead to issues such as leaky gut and poor digestion.
6. Influences Gut Microbiome Balance
Additionally, calcium helps maintain a healthy balance of gut bacteria. These beneficial bacteria support digestion, make nutrients, and boost immune health. If calcium is lacking, this balance may shift, causing discomfort or irritation in the gut.
7. Prevents Constipation When Balanced
Calcium supports normal bowel movements by helping the muscles in the colon work correctly. However, too much calcium, especially from supplements, can lead to constipation. That’s why it’s important to balance calcium with enough water and other minerals like magnesium.
8. Reduces Gut Inflammation
It also helps reduce irritation in the digestive tract. Calcium strengthens the immune system, which can help calm gut irritation. When calcium intake is adequate, it may ease symptoms of IBS or bloating.
9. Boosts Energy for Digestive Processes
Calcium supports cellular energy production, which powers cellular functions, including digestion. Every part of the digestive system, from muscle contractions to enzyme activity, needs energy to function. Without enough calcium, your digestion may become sluggish and less efficient.
10. Supports Hormone and Nerve Signals in the Gut
Calcium helps your nerves send signals that control digestion and hormone release. These signals tell your body when to produce saliva, stomach acid, and bile. Poor calcium levels can disrupt this communication, leading to slow or uneven digestion.
Conclusion
Calcium supports your gut in many ways. It keeps digestive muscles active, helps enzymes break down food, and supports nutrient absorption and gut strength. Still, balance is key. Consuming too little calcium can slow digestion, while excessive calcium intake can lead to constipation. To support your gut, try to get calcium from a variety of foods and be mindful of your supplement use.
The best way to support your digestive system is to obtain calcium from natural food sources, such as dairy products, leafy greens, and fortified plant milk. If you use supplements, use them with care and monitor your intake closely.
Frequently Asked Questions
Can calcium improve digestion?
Yes, calcium helps improve digestion by supporting muscle contractions in the gut, activating digestive enzymes, and regulating stomach acid. It plays a crucial role in moving food through the intestines and facilitating the effective absorption of nutrients by your body.
Does calcium cause constipation?
It can, especially when taken in large amounts through supplements. While calcium supports bowel regularity, excess intake without adequate hydration or magnesium may lead to constipation.
What’s the best way to get calcium for digestive health?
Whole food sources, such as leafy greens, dairy products, almonds, and fortified plant-based milk, are best. These foods provide calcium, along with fiber and other essential nutrients, that aid digestion and support gut health.
How does calcium interact with other digestive nutrients?
Calcium works best in conjunction with vitamin D for optimal absorption and utilization. However, it can interfere with the absorption of other minerals, such as iron, magnesium, and zinc, if consumed in high doses. Balance is key for optimal digestive function.